How to Build a RAG-Powered Application: Step-by-Step Process and Cost Breakdown
Table of Contents
Subscribe To Our Newsletter

Artificial intelligence isn’t slowing down. By 2025, Gartner estimates that 80% of enterprises will have used generative AI APIs or deployed apps built on large language models. IDC says global AI spending will top $500 billion in 2027. But here’s the rub: most businesses aren’t sure if the AI they’re investing in will give them accurate, trustworthy results.
That’s where RAG-powered applications step in. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is the bridge between the imagination of an LLM and the factual backbone of your enterprise data. It’s like pairing a brilliant storyteller with a fact-checking librarian. You get creativity and precision working hand in hand.
Now, let’s be real. Businesses today don’t just want flashy chatbots. They want tools that understand their data, reduce hallucinations, and actually make employees’ lives easier. Honestly, who hasn’t been stuck on hold with a customer service bot that repeats the same irrelevant line? With RAG, that gap gets closed.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through what a RAG-powered application is, how the RAG development process works, and yes, what it really costs to build one. Because cost matters. And here’s the thing: the budget question isn’t always about what you pay upfront, it’s about the long-term upkeep too. Stick with me, we’re diving deep.
What is a RAG-Powered Application?
Think of a standard LLM as a talented intern who’s great at drafting ideas but sometimes gets the facts wrong. Now imagine giving that intern access to your company’s knowledge base, legal documents, research library, or financial records and making them check before answering. That’s essentially a RAG-powered application.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation combines:
- Retrieval – searching a vector database for RAG apps or knowledge source to find the most relevant information.
- Generation – passing that retrieved data into the LLM to generate accurate, context-specific answers.
Why are businesses leaning toward this model? Because RAG reduces hallucinations (those moments when AI just makes stuff up), keeps answers grounded in real data, and makes enterprise AI truly useful. From RAG chatbot development in customer service to compliance tools in finance, companies see better ROI when the answers align with domain knowledge.
Put simply: if you want enterprise RAG solutions that talk less fantasy and more fact, RAG is the route forward.
Step-by-Step Process to Develop a RAG-Powered Application
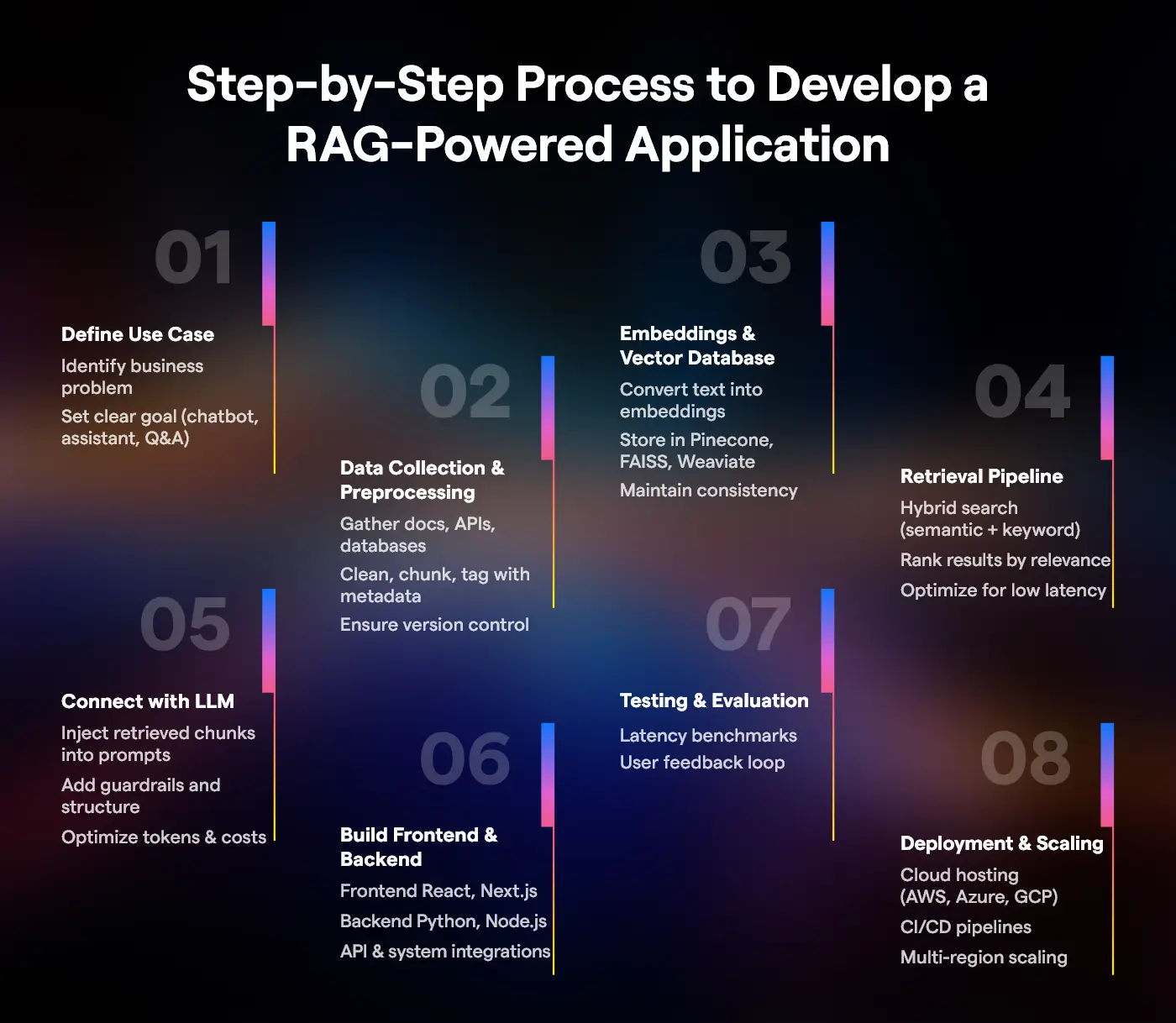
1. Define the Use Case
Before you build anything, clarify the “why.” Do you need a legal Q&A bot? A RAG-powered application for healthcare solutions insights? Or maybe an internal knowledge assistant for employees? The sharper your use case, the more focused your RAG pipeline becomes.
Want to skip the trial-and-error?
Our team at Codiant AI builds RAG application workflows customized for your business domain.
Book a free consultation today.
2. Data Collection & Preprocessing
This step can make or break your RAG-powered application. Data flows in from all kinds of places: PDFs, Word docs, websites, CRMs, knowledge bases, even live APIs. But here’s the thing—raw data is messy. You can’t just dump it into a model and hope for magic. It has to be cleaned, reshaped, and made machine-ready.
And let’s be real, this isn’t just “tidy up the text.” Preprocessing has layers:
- File formats matter. PDFs with complex layouts? They’ll need custom parsing. Scanned docs? OCR to the rescue. Each format comes with quirks.
- Metadata is gold. Tagging documents with source, author, or timestamp makes retrieval smarter. A RAG app in healthcare, for example, should know to pull the 2024 study, not one from 2009.
- Chunking strategy isn’t random. Cutting text into 300-token chunks versus 600 changes everything. Overlap between chunks prevents context gaps.
- Consistency in embeddings. Switching embedding models halfway can wreck retrieval. Pick one and stay loyal.
- Quality filters save headaches. Duplicates, boilerplate footers, irrelevant disclaimers—they all clutter your vector store and confuse retrieval. Strip them out early.
- Versioning matters. Enterprises forget this. Data changes, regulations shift, policies get updated. If your system doesn’t version data, users may get outdated (and wrong) answers.
So yes, preprocessing is where the RAG development process shows its teeth. Do it right, and your app retrieves exactly the chunk you want. Do it sloppy, and the model confidently spits out nonsense. And that’s not the kind of “AI surprise” anyone’s signing up for.
3. Choose Embedding Model & Vector Database
Once your data is prepped, it’s time to give it a “GPS coordinate” in semantic space. That’s what embeddings do: they turn chunks of text into math vectors that let the system figure out, “Hey, this passage is 87% similar to that user query.” Without embeddings, retrieval is basically guessing.
Now, here’s where choices get tricky:
- Pick the right embedding model. OpenAI, Cohere, Hugging Face, Google—they all have solid options. Some are lightning fast but shallow, others are slower but capture nuance better. It depends on your use case. A legal assistant needs precision. A customer support bot may trade nuance for speed.
- Vector databases aren’t all created equal. Pinecone, Weaviate, Milvus, FAISS… each has strengths. Pinecone scales like crazy for enterprise workloads. FAISS is open-source and free but needs more engineering lift. Weaviate adds built-in hybrid search (semantic + keyword) that saves time.
- Don’t ignore indexing strategy. Flat indexes are simple but slow at scale. ANN (Approximate Nearest Neighbor) indexing speeds up search for massive datasets. That’s vital if you’re building a RAG-powered application that needs answers in milliseconds.
- Metadata filtering is your best friend. Imagine searching not just by meaning but also by “documents authored after 2021” or “files tagged finance.” That’s the kind of precision businesses expect.
- Consistency again matters. Embeddings must be generated with the same model across your entire dataset. Mixing them is like measuring distance in miles for half the data and kilometers for the other half. Retrieval will get messy.
So, think of embeddings as the brain wiring and the vector DB as the filing cabinet. If either is poorly chosen, your RAG app turns into that co-worker who always says, “I think I saw it somewhere,” but never actually finds the file.
4. Integrate the Retrieval Pipeline
Here’s the heart of a RAG-powered application: the retrieval pipeline. Think of it as the “librarian” in your system. When a user asks a question, the pipeline decides which chunks of data to grab from the vector store and hand over to the LLM. Effective AI personalization ensures the retrieved data is tailored to each user, improving relevance and accuracy. If this step fails, the LLM is basically writing with no references. And we all know what happens then: confident nonsense.
Here’s what really matters in retrieval design:
- Query parsing matters more than you think. A user’s “simple” question often needs translation into embeddings, filters, or even keyword queries before it touches the database. Skip this, and you miss the intent.
- Hybrid search is the sweet spot. Pure semantic search is good but not perfect. Pairing it with traditional keyword matching (BM25) often produces sharper results. Example: a medical query might rely on the keyword “insulin” while the semantic engine picks up related context like “glucose regulation.” Together, they win.
- Ranking and scoring aren’t optional. The pipeline doesn’t just grab documents; it ranks them. Which passage is more relevant? Which is more recent? Without ranking logic, retrieval feels random.
- Latency kills. Users expect sub-second responses. That means optimizing ANN indexes, caching frequent queries, and trimming down data noise. A 4-second pause feels like eternity in chat.
- Context window balancing. Feed too little into the LLM and it answers vaguely. Feed too much and you hit token limits (or rack up API costs). Smart retrieval strikes the balance.
At its best, the retrieval pipeline is invisible, users just get sharp, accurate answers. But behind the curtain, it’s a delicate dance of query understanding, filtering, ranking, and optimization. Get it wrong, and your shiny new app becomes that search tool everyone avoids because “it never finds the right thing.”
Looking to accelerate your RAG application development?
Codiant AI delivers production-ready apps with faster turnaround and lower cost overhead.
Let’s talk today.
5. Connect with the LLM
Here’s where the magic happens. Once your retrieval pipeline fetches the right chunks, those passages get injected into a prompt and handed off to an LLM. The LLM is the storyteller, but with retrieval in play, it’s no longer winging it — it’s telling stories with receipts.
Some key realities at this stage:
- Model choice matters. GPT-4, Claude, Llama, Mistral — each has quirks. Some are better at creative reasoning, others at precise fact-based answers. Choose based on your use case, not hype.
- Prompt engineering isn’t fluff. How you frame the retrieved data inside the prompt changes everything. A sloppy prompt can still trigger hallucinations. Structured prompts (like “Answer only using the provided context”) keep the LLM grounded.
- Guardrails are your safety net. Enterprises can’t risk an LLM going rogue, which is why filters, fallback responses, and rejection rules are essential when context is missing. In workflows supported by RPA services, a clear “I don’t know” is far safer than an answer that could create compliance risks.
- Cost is real. Every token you send through the LLM adds up. The tighter and cleaner your retrieval, the less you spend.
Bottom line: the LLM is the face of your RAG-powered application. It’s what users interact with, and it either builds trust or breaks it.
6. Build Frontend & Backend
Now we’re talking user experience. The pipeline might be slick, but if the interface feels clunky, adoption tanks. Your RAG application development must balance accuracy with intuitive design, leveraging NLP to ensure interactions feel natural, responsive, and genuinely useful for end users.
Here’s what counts:
- Frontend frameworks. React, Next.js, Vue — take your pick. The goal is a clean interface where users can interact naturally. Chat-style UIs are popular, but dashboards and widgets work too.
- Backend glue. Python with FastAPI or Django, Node.js with Express, or even Go if performance is critical. The backend is where requests flow, APIs connect, and your RAG stack gets orchestrated.
- APIs and middleware. Most enterprise builds need connectors into CRMs, ERPs, or document management systems. That means clean APIs, proper authentication, and security baked in.
- Latency optimization. Nobody wants to wait 5 seconds for an answer. Frontend caching, async requests, and smart backend design all trim response times.
- Scalability thinking early. Even if you start with 100 users, plan for 10,000. A backend that crumbles under load will undo all the smart retrieval and LLM work you’ve done.
So yes, building the frontend and backend is “just software development,” but here’s the twist: the way they handle context, speed, and scale determines if your RAG app feels like a polished assistant or a clumsy prototype.
7. Testing & Evaluation
Here’s where reality checks kick in. A RAG-powered application might look shiny on the surface, but if the answers are wrong, laggy, or just plain weird, users won’t trust it. Testing isn’t optional — it’s survival.
What you need to test:
- Accuracy, not vibes. Does the model actually pull the right facts? Enterprises often build custom evaluation sets to measure precision and recall.
- Hallucination rate. Every LLM drifts into fiction now and then. Your job is to measure how often and fix it before it hits production.
- Latency benchmarks. Anything over two seconds feels slow in chat. Stress-test your pipeline to make sure it responds quickly under load.
- User acceptance. Let’s be real: you can’t just rely on metrics. Put it in front of real users, gather feedback, and iterate. A finance team might hate vague answers. A support team might need shorter, sharper responses.
- Continuous monitoring. Testing isn’t a one-time box to check. Models drift, data changes, APIs update. Without ongoing evaluation, accuracy decays.
If you skip rigorous testing, you risk building the AI version of a customer support bot that says “I understand” but never actually solves the problem. Nobody wants that.
8. Deployment & Scaling
Deployment is when your RAG app goes from experiment to enterprise tool. And here’s the truth: the first rollout is rarely the hardest part. It’s what comes next — scaling — that separates a cool demo from a mission-critical system.
Key things to nail:
- Cloud platforms. AWS, Azure, GCP — each has managed services for vector databases, model hosting, and scaling infrastructure. Choose based on your stack and compliance needs.
- CI/CD pipelines. Continuous integration and deployment ensure new data, model updates, or bug fixes roll out without downtime. Enterprises don’t forgive outages.
- Monitoring and logging. It’s not just uptime — you need insights into latency, error rates, API costs, and retrieval accuracy. Without observability, scaling becomes guesswork.
- Cost control. At scale, tokens and queries add up fast. Smart teams use caching, batching, and prompt optimization to keep usage in check.
- Global scale. If your audience spans regions, edge deployment and multi-region vector DB replicas keep latency down. No user in Singapore wants to wait while your system pings Virginia.
Scaling isn’t just about handling more traffic. It’s about keeping performance sharp, costs predictable, and trust intact as the app grows.
Cost to Develop a RAG-Powered Application
Now, the million-dollar (sometimes literally) question: how much does it cost? The answer depends on complexity.
Prototype or MVP ($15,000 – $40,000)
- Simple RAG chatbot development with a small knowledge base.
- Best for proof-of-concepts and internal demos.
- Uses open-source embeddings and free-tier databases.
Mid-Level Application ($50,000 – $120,000)
- Handles larger datasets.
- Integrates with CRM, HR, or ERP systems.
- Needs RAG development cost breakdown planning—APIs, storage, and cloud costs add up.
Enterprise-Grade Solution ($150,000 – $300,000+)
- Multi-language support, compliance features, custom integrations.
- Live monitoring, hybrid retrieval, and scalable architecture.
- Built for regulated industries like finance, healthcare, or law.
Beyond build cost, factor in ongoing expenses:
- API usage (LLM queries).
- Vector database storage.
- Cloud hosting and DevOps support.
The truth? Cost to build applications is less about upfront development and more about long-term usage patterns.
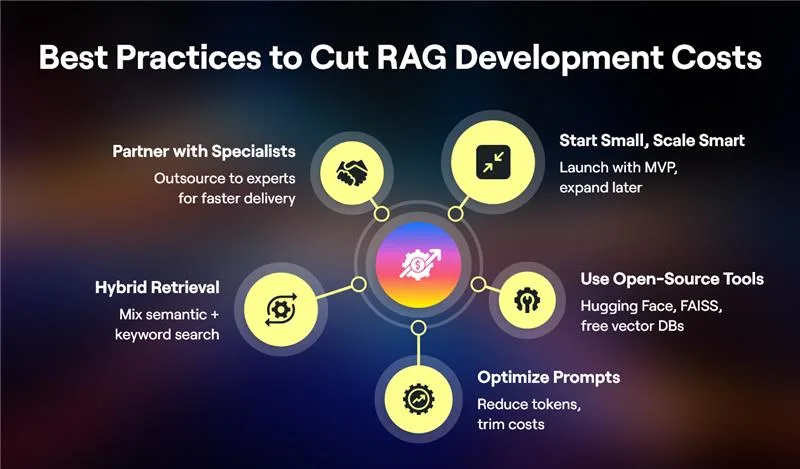
Best Practices for Building Cost-Effective RAG Applications
- Start small, scale smart: Launch with an MVP before expanding to enterprise scale.
- Leverage open-source tools: Hugging Face models, FAISS, and open-source vector stores cut costs.
- Optimize prompts: Fewer tokens = lower API bills.
- Hybrid retrieval strategies: Combine semantic search with keyword matching to improve accuracy.
- Partner with specialists: Outsourcing to enterprise RAG solutions providers ensures expertise without hiring in-house teams.
Following these practices lowers both RAG application development costs and operational headaches.
Read More:- AI-Powered Telemedicine: Must-Know Apps and Cost Breakdown
Why Choose Codiant AI as Your Development Partner?
Codiant AI has a proven track record in RAG-powered application builds for enterprises across healthcare, finance, and retail. Our team understands how AI strategy consulting in USA organizations must address the “hallucination tax” that many businesses face when deploying AI applications at scale. By combining deep expertise in LangChain-based RAG pipelines, advanced LLM integration, and scalable cloud architecture, we deliver solutions that meet enterprise-grade accuracy, performance, and compliance requirements.
With Codiant, you don’t just build a RAG app, you build a long-term competitive advantage.
Don’t just read about RAG-powered applications
Put one to work for your business.
Get in touch with Codiant AI today.
Frequently Asked Questions
An application powered by RAG, or Retrieval-Augmented Generation, pairs large language models with external sources of knowledge. Instead of a purely pre-trained model, it retrieves the most relevant info from databases (that can also include documents or even APIs) and generates answers that are contextual to such retrievals. This method increases precision, minimizes hallucinations, and increases the dependability of AI systems for verticals such as healthcare, finance, retail, and legal services.
Large language models can generate answers that sound plausible but are actually completely wrong, a phenomenon called hallucinations. RAG addresses this downside by grounding responses in newly acquired data from the time of generation. The system can fetch verified information from vector databases or knowledge bases, do prompt injection and steer the model to produce factually accurate results. This retrieval plus generation mechanism guarantees that the answers are not only correct, on-topic, and context-aware, but also explainable and verifiable, lowering the risk of releasing an incorrect response to a fraction of a percent.
The price relies on the complexity, the data dimension, and all the built-in integrations. A basic MVP prototype will run between 15,000–40,000, a mid-range app 50,000–120,000+ and enterprise-grade systems up to 150,000–300,000+. Recurrences costs includes storage ( vector database ), LLM API calls and Cloud hosting. When budgeting for RAG application development, businesses should not only consider the initial build cost but also long-term operational costs.
The timeline to develop the websites can vary based on scope and complexity. 6–10 weeks to build an MVP/proof of concept. Mid-level applications require around 3–4 months while Enterprise-grade projects may last around 6–8+ months because features such as compliance, multi-language support, and integrations ramp up the time in coding and testing. Engaging with a well-established RAG development company ensures that the time-to-market is minimized without quality being compromised.
Yes. Applications that are fueled by RAG are built to connect to CRMs, ERPs, HR platforms, knowledge bases, and even bespoke APIs. They can be rolled out for enterprises that want to scale existing infrastructure. Using the right tech stack — usually LangChain for orchestration, vector db for retrieval or cloud platforms such as AWS or Azure and all this works together — it is possible for business to embed RAG transparently in the existing workflow while scaling on top.
Featured Blogs
Read our thoughts and insights on the latest tech and business trends
10 Agentic AI Use Cases Powering Enterprise ROI in 2026
- February 20, 2026
- AI Agent Development
In a Nutshell: Agentic AI goes beyond traditional automation by making goal-driven decisions across complex enterprise workflows. In 2026, enterprises are adopting agentic AI for measurable ROI, not experimentation or pilots. Agentic AI use cases... Read more
AI in Business Intelligence- The 2026 Roadmap to Data Dominance
- February 16, 2026
- AI-Powered Data Analytics
Business intelligence was built to bring clarity to complex businesses. Dashboards, reports, KPIs and scorecards were meant to help leaders see what was happening and make informed choices. In practice, most BI systems still focus... Read more
Top 20 Generative AI Development Companies in the USA (2026)
- February 9, 2026
- Generative AI
Generative AI is no longer something companies “try out.” In 2026, it is something they depend on. US businesses now use generative AI to build products faster, automate everyday work, and make better decisions. AI... Read more




